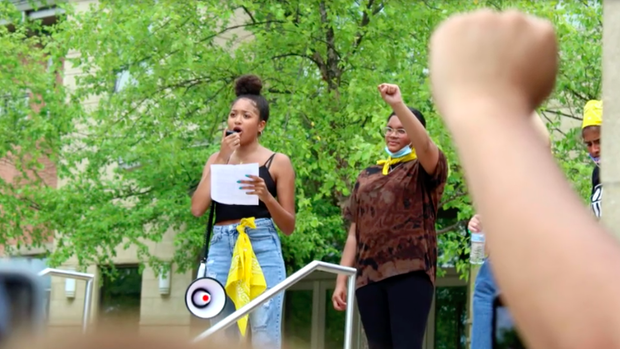When Americans think of the Civil Rights Movement, they think of icons like Martin Luther King Jr. and John Lewis — men with such a gift for oration that the words of their speeches are forever ingrained in American history. Today, however, there is no central leader unifying the marches and rallies for racial justice across America.
There is no shortage of passionate young activists, nor is there a shortage of inspiration for change. The makeup of the movement simply looks different. And while it is often criticized for being decentralized, some of the young activists at its core tell CBS News that that's actually by design.
"I think that this movement doesn't need a central leader," 23-year-old Chelsea Miller, who co-founded Freedom March NYC in the wake of George Floyd's killing, told CBS News. "Because when you cut off one head, there are still dozens, hundreds, thousands of heads operating. … There isn't one leader and I think there's a beauty to that."
In 1955, the brutal murder of 14-year-old Emmett Till in Mississippi and the acquittal of his killers by an all-White jury served as the spark that motivated a generation of young activists, like John Lewis and Rosa Parks, to change the course of history.
The young activists of today have many sparks. Many Emmett Tills.
"Every single uprising that took place in the 1960s, they involved the unjust killing by the police of an unarmed black man as the spark," said Marc Morial, president of the National Urban League, in the CBS News special, "The Power of August."
"Trayvon [Martin] and Michael Brown, Tamir Rice, Eric Garner, were and are this generation's Emmett Tills. And I say, 'Tills' because I use it in the plural."
For 29-year-old St. Louis native Kayla Reed, the spark was Michael Brown.
In August 2014, when Brown's killing set the city of Ferguson, Missouri ablaze, she was a pharmacy technician. Now, she's one of the top activists in the national movement for police accountability.
"People were dealing with over-policing. They were dealing with a bunch of fines and fees. They were dealing with the impacts of cash bail. It highlighted all the things that needed to change," she told CBS News. "I went from following the person with the bullhorn to being the person with the bullhorn."
Reed is far from alone. After Ferguson, organizers who had been working in the racial justice space for decades noticed that the makeup of the movement began to change.
"The protesting community was suddenly much younger and there were new people on the streets," said John Chasnoff. "This younger generation, they wanted to shake things up in a way that would actually disrupt the current status quo systems."
Suddenly, not only were there younger faces at the protests, there were women at their helm.
Black Lives Matter was founded by two women. Women like Miller and Reed were called to action by the deaths of Black men at the hands of police. And soon, the teenage girls of Generation Z began joining the movement, as well.
For 17-year-old Mariah Norman, the spark was learning in her AP Government class that voter suppression still affected Black and Brown communities throughout the United States.
"We had to choose a social issue," she told CBS News national correspondent Michelle Miller. "And the one that I chose was voter suppression, just because I was like, 'I didn't know that that was still a thing.'"
The Mason, Ohio high school student is not even old enough to vote, yet she's already joining the cause — adding her name to a long list of women who are tackling America's racial justice issues head-on.
"Voting is really important to me because I feel like young people in general, it seems like the laws and the policies that dictate our everyday lives are just things that we have to follow," she said. "I don't think that it has to be that way. And I think that the youth vote is so incredibly important, and getting young people excited about what goes on in their government and, you know, being a part of that democracy."
Women have been pivotal to the civil rights movement since the 1960s, but they've never owned the microphone or held the reins quite like they do today.
"This is a moment when the voice, particularly of Black women, is not only being heard, it is really commanding the stage," said Sherrilyn Ifill, president of the NAACP Legal Defense Fund. "It's our time."
Tears streamed down Brooke Moreland’s face as she watched tens of thousands gather on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial to decry systemic racism and demand racial justice in the wake of several police killings of Black Americans.
But for the Indianapolis mother of three, the fiery speeches delivered Friday at the commemoration of the 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom also gave way to one central message: Vote and demand change at the ballot box in November.
“As Black people, a lot of the people who look like us died for us to be able to sit in public, to vote, to go to school and to be able to walk around freely and live our lives,” the 31-year-old Moreland said. “Every election is an opportunity, so how dare we not vote after our ancestors fought for us to be here?”
That determination could prove critical in a presidential election where race is emerging as a flashpoint. President Donald Trump, at this past week’s Republican National Convention, emphasized a “law and order” message aimed at his largely white base of supporters. His Democratic rival, Joe Biden, has expressed empathy with Black victims of police brutality and is counting on strong turnout from African Americans to win critical states such as North Carolina, Florida, Pennsylvania, and Michigan.
As the campaign enters its latter stages, there’s an intensifying effort among African Americans to transform frustration over police brutality, systemic racism, and the disproportionate toll of the coronavirus into political power. Organizers and participants said Friday’s march delivered a much-needed rallying cry to mobilize.
“If we do not vote in numbers that we’ve never ever seen before and allowed this administration to continue what it is doing, we are headed on a course for serious destruction,” Martin Luther King III told The Associated Press before his rousing remarks, delivered 57 years after his father’s famous “I Have A Dream” speech. “I’m going to do all that I can to encourage, promote, to mobilize and what’s at stake is the future of our nation, our planet. What’s at stake is the future of our children.”
As speakers implored attendees to “vote as if our lives depend on it,” the march came on the heels of yet another shooting by a white police officer of a Black man – 29-year-old Jacob Blake in Kenosha, Wisconsin, last Sunday — sparking demonstrations and violence that left two dead.
“We need a new conversation … you act like it’s no trouble to shoot us in the back,” the Rev. Al Sharpton said. “Our vote is dipped in blood. We’re going to vote for a nation that stops the George Floyds, that stops the Breonna Taylors.”
Navy veteran Alonzo Jones- Goss, who traveled to Washington from Boston, said he plans to vote for Biden because the nation has seen far too many tragic events that have claimed the lives of Black Americans and other people of color.
“I supported and defended the Constitution and I support the members that continue to do it today, but the injustice and the people that are losing their lives, that needs to end,” Jones-Goss, 28, said. “It’s been 57 years since Dr. King stood over there and delivered his speech. But what is unfortunate is what was happening 57 years ago is still happening today.”
Drawing comparisons to the original 1963 march, where participants then were protesting many of the same issues that have endured, National Urban League President and CEO Marc Morial said it’s clear why this year’s election will be pivotal for Black Americans.
“We are about reminding people and educating people on how important it is to translate the power of protest into the power of politics and public policy change,” said Morial, who spoke Friday. “So we want to be deliberate about making the connection between protesting and voting.”
Nadia Brown, a Purdue University political science professor, agreed there are similarities between the situation in 1963 and the issues that resonate among Black Americans today. She said the political pressure that was applied then led to the Voting Rights Act of 1965 and other powerful pieces of legislation that transformed the lives of African Americans. She’s hopeful this could happen again in November and beyond.
“There’s already a host of organizations that are mobilizing in the face of daunting things,” Brown said. “Bur these same groups that are most marginalized are saying it’s not enough to just vote, it’s not enough for the Democratic Party or the Republican Party to ask me for my vote. I’m going to hold these elected officials that are in office now accountable and I’m going to vote in November and hold those same people accountable. And for me, that is the most uplifting and rewarding part — to see those kinds of similarities.”
But Brown noted that while Friday’s march resonated with many, it’s unclear whether it will translate into action among younger voters, whose lack of enthusiasm could become a vulnerability for Biden.
“I think there is already a momentum among younger folks who are saying not in my America, that this is not the place where they want to live, but will this turn into electoral gains? That I’m less clear on because a lot of the polling numbers show that pretty overwhelmingly, younger people, millennials and Gen Z’s are more progressive and that they are reluctantly turning to this pragmatic side of politics,” Brown said.
That was clear as the Movement for Black Lives also marked its own historic event Friday — a virtual Black National Convention that featured several speakers discussing pressing issues such as climate change, economic empowerment, and the need for electoral justice.
“I don’t necessarily see elections as achieving justice per se because I view the existing system itself as being fundamentally unjust in many ways and it is the existing system that we are trying to fundamentally transform,” said Bree Newsome Bass, an activist, and civil rights organizer, during the convention’s panel about electoral justice. “I do think voting and recognizing what an election should be is a way to kind of exercise that muscle.”
Black Lives Matter organizers in Kenosha, Wisconsin held a rally and march, following the shooting of Jacob Blake by police in front of three of his children earlier this week https://t.co/Pwf8sZfg5a pic.twitter.com/wiiBjW8C7W
— Reuters (@Reuters) August 30, 2020
President Trump comments on #JacobBlake and a second shooting in the community by a 17-year-old that left 2 dead and one injured pic.twitter.com/QdlRUCtH4b
— Bloomberg QuickTake (@QuickTake) August 29, 2020
“I am the keeper now watch me reign. Hear my roar.”#JacobBlake’s sister, Letetra Widman, recited a new spoken word piece at a #JusticeforBlake march in Kenosha, Wisconsin pic.twitter.com/r5kWauRhPG
— Bloomberg QuickTake (@QuickTake) August 29, 2020
“You cannot imagine what it feels like to look at your baby, paralyzed from the waist down, shackled ... where was my son going? They already put him in the bed.”
— Bloomberg QuickTake (@QuickTake) August 29, 2020
Jacob Blake Sr. talked about the 2 different justice systems in America during a #JusticeforBlakeMarch pic.twitter.com/yeDxKwJykk