In September 2024, the euro area seasonally-adjusted unemployment rate was 6.3%, stable compared with August 2024 and down from 6.6% in September 2023. The EU unemployment rate was 5.9% in September 2024, also stable compared with August 2024 and down from 6.1% in September 2023. These figures are published by Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union.
Eurostat estimates that 13.042 million persons in the EU, of whom 10.884 million in the euro area, were unemployed in September 2024.
Compared with August 2024, unemployment increased by 61 thousand in the EU and by 13 thousand in the euro area.
Compared with September 2023, unemployment decreased by 226 thousand in the EU and by 330 thousand in the euro area.
Youth unemployment
In September 2024, 2.861 million young persons (under 25) were unemployed in the EU, of whom 2.287 million were in the euro area. In September 2024, the youth unemployment rate was 14.8% in the EU, up from 14.5% in August 2024, and 14.4% in the euro area, up from 14.3% in the previous month.
Compared with August 2024, youth unemployment increased by 44 thousand in the EU and by 10 thousand in the euro area.
Compared with September 2023, youth unemployment decreased by 16 thousand in the EU and by 68 thousand in the euro area.
Unemployment by sex
In September 2024, the unemployment rate for women was 6.1% in the EU, stable compared with the previous month, and the unemployment rate for men was 5.8%, up from 5.7% in August 2024. In the euro area, the unemployment rate for women was 6.5%, stable compared with the previous month, and the unemployment rate for men was 6.1%, also stable compared with August 2024.
Additional labour market indicators
The estimates in this News Release are based on the globally used International Labour Organisation (ILO) standard definition of unemployment, which counts as unemployed people without a job who have been actively seeking work in the last four weeks and are available to start work within the next two weeks.
To capture in full the labour market situation, the data on unemployment have been complemented by additional indicators, e.g. underemployed part-time workers, persons seeking work but not immediately available and persons available to work but not seeking, released together with LFS data for the second quarter of 2024.
LFS data for the third quarter of 2024 will be released on 13 December 2024.
Tables
Euro area annual inflation is expected to be 2.0% in October 2024, up from 1.7% in September according to a flash estimate from Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union.
Looking at the main components of euro area inflation, services is expected to have the highest annual rate in October (3.9%, stable compared with September), followed by food, alcohol & tobacco (2.9%, compared with 2.4% in September), non-energy industrial goods (0.5%, compared with 0.4% in September) and energy (-4.6%, compared with -6.1% in September).
Tables
Notes for users
Revisions and timetable
The euro area inflation flash estimate is issued at the end of each reference month.
The complete set of harmonized indices of consumer prices (HICP) for the euro area, EU, and Member States is released around the middle of the month following the reference month.
The next release with full data for October 2024 is scheduled for 19 November 2024.
Methods and definitions
Annual inflation is the change in the price level of consumer goods and services between the current month and the same month of the previous year. Monthly inflation is the change in the price level between the current month and the previous month.
Geographical information
The euro area consists of Belgium, Germany, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Spain, France, Croatia, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Austria, Portugal, Slovenia, Slovakia and Finland.
The euro area data refers to the country composition at a specific point in time. Changes in the composition of the euro area are incorporated using a chain index formula.
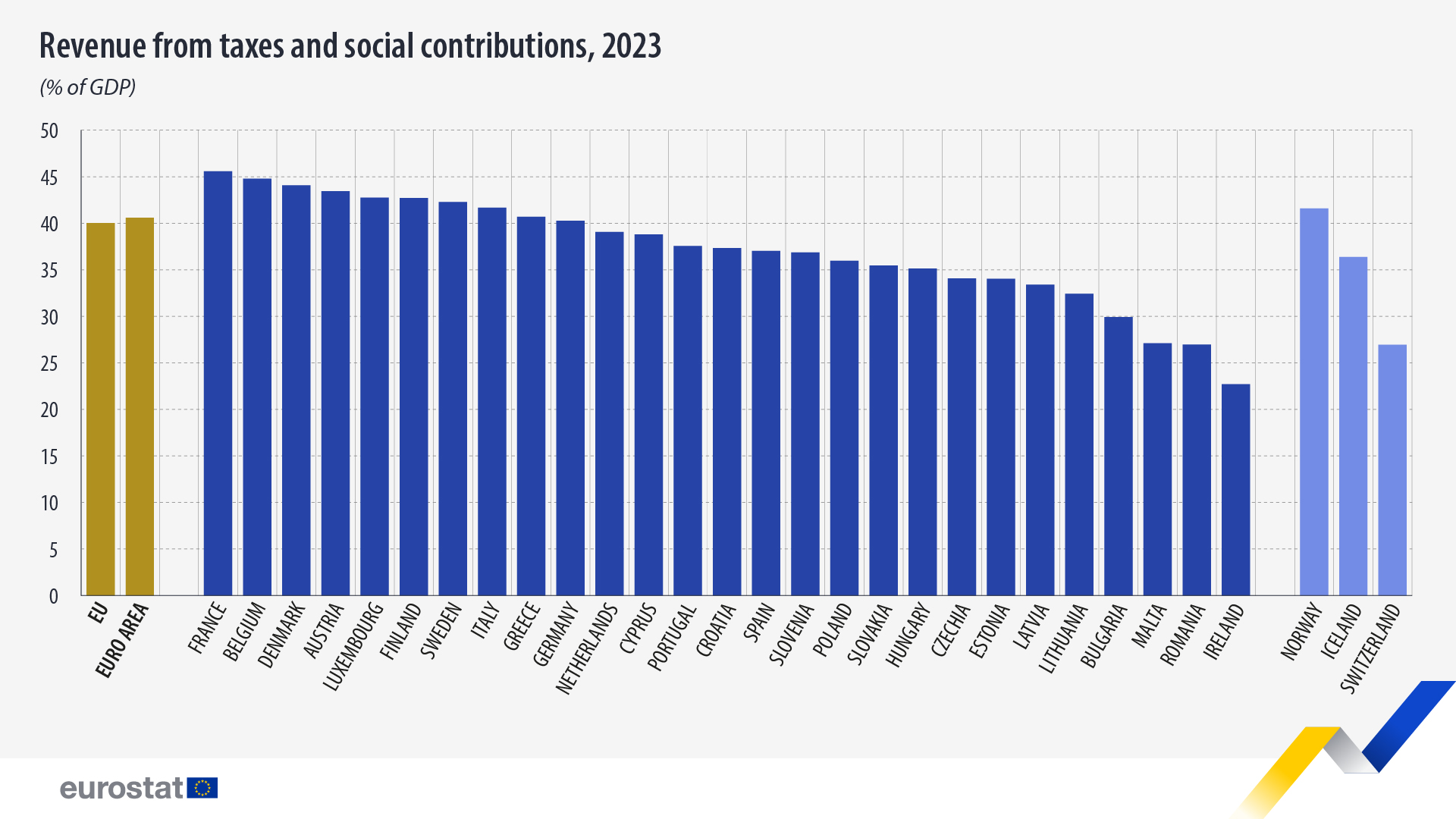
The overall tax-to-GDP ratio, meaning the sum of taxes and net social contributions as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP), stood at 40.0% in the EU in 2023, a decrease compared with 2022 (40.7%). In the euro area, the tax-to-GDP ratio also decreased from 41.4% in 2022 to 40.6% in 2023.
In absolute terms, in 2023, revenue from taxes and social contributions increased by €308 billion in the EU compared with 2022, to stand at €6 883 billion.
This information comes from data on taxation published by Eurostat today. This article presents some findings from the more detailed Statistics Explained article.
Highest tax-to-GDP ratio in France, Belgium and Denmark
The tax-to-GDP ratio varied significantly between EU countries in 2023, with the highest shares of taxes and social contributions as a percentage of GDP being recorded in France (45.6%), Belgium (44.8%) and Denmark (44.1%).
At the opposite end of the scale, Ireland (22.7%), Romania (27.0%) and Malta (27.1%) registered the lowest ratios.
Source dataset: gov_10a_taxag
Largest increases of tax-to-GDP ratios in Cyprus and Luxembourg
In 2023, compared with 2022, the tax-to-GDP ratio increased in 11 EU countries, with the largest increases being observed in Cyprus (from 35.9% in 2022 to 38.8% in 2023) and Luxembourg (40.2% in 2022 and 42.8% in 2023).
In contrast, decreases of more than 0.1 percentage points of GDP were recorded in 12 EU countries, with the largest decreases noted in Greece (from 42.8% in 2022 to 40.7% in 2023) and France (from 47.6% in 2022 to 45.6% in 2023).
Source dataset: gov_10a_taxag